· Sustainloop editorial team · regional-ecosystems · 4 min read
Smart Specialization Strategy
Regional priorities and alignment with energy transition of energy intensive industries

Conceived within the reformed Cohesion policy of the European Commission, Smart Specialisation is a place-based approach to innovation policy that identifies and supports strategic areas for intervention based on the strengths and potential of a region’s economy. It is a forward-looking approach that embraces a broad view of innovation, including technology-driven, practice-based, and social innovation. At its core, a Smart Specialization Strategy (S3) is about identifying and supporting the areas where a region can excel and grow based at the region’s unique assets, capabilities, and opportunities. S3 prioritize areas where regions or countries have a competitive advantage, the potential for knowledge-driven growth, and the ability to address societal and environmental challenges. The specific priorities identified vary from region to region, and in the course of time they are adjusted as needed.
Here we present the established priorities set for the period 2021-2027 in the regions of the 5 demo cases in TRINEFLEX, that are associated with the specific process industries and the regional energy transition goals. From studying the identified priorities, it is clear that in each region the smart specialization strategy is strongly attached with the industrial actors. Resource and energy intensive industries have an important effect and leading role in promoting green and sustainable innovation in the wider area they are established. By actively engaging with local actors, including businesses, research institutions, government bodies, and communities, industries can create dynamic synergies that drive sustainable innovation. These collaborations have the potential to enhance economic development, environmental conservation, and the overall well-being of local and regional ecosystems. The key lies in fostering partnerships that prioritize sustainability and responsible resource management while exploiting the potential of local economic activities that usually have a history of many decades in the area.
Industrial and industrial-urban symbiosis can also act as a catalyst in promoting sustainability and addressing local environmental challenges. Key benefits include resource optimization, development of new business models, local economic growth, urban resilience, shared responsibility, and increased community engagement. These approaches encourage further collaboration, energy and resources efficiency, and the adoption of circular economy practices, ultimately fostering a more sustainable and resilient relationship among industries as well as between industries and the urban ecosystem.
TRINEFLEX Demo Cases | Established regional priorities 2021-2027 | |
|---|---|---|
 Basque Country (ES21), Spain Basque Country (ES21), Spain | 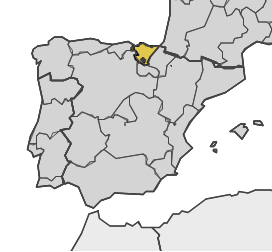 | • Smart Industry (Digital transformation, efficient use of material and energy resources, sustainable production, exploitation of data) • Cleaner Energy (Renewable energy, green technologies, energy transition, clean energy chains, digital transformation) • Eco-innovation (Sustainable technology, environmental impact assessment, circular economy solutions, green innovation, climate resilience) • Sustainable cities (Smart cities, urban resilience, circular economy, digital transformation, healthy cities) |
 Region of Murcia (ES62), Spain Region of Murcia (ES62), Spain | 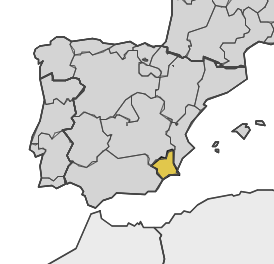 | • Agri-food (Agriculture, Livestock, Fishing, Water cycle, Environment, Logistics and Transportation) • Core Activities (Energy, Marine and Maritime, Chemistry) • Quality of life (Tourism, habitat, health, footwear and fashion) |
 Veneto (ITH3), Italy Veneto (ITH3), Italy | 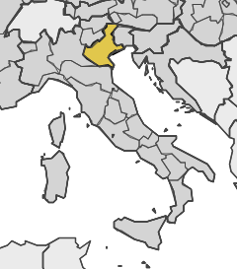 | • Smart Manufacturing (Intelligent management of production systems, Digital Twin solutions; Treatment and/or reuse of industrial waste; Innovative materials and components; Tools for the sustainable supply chain and “green” energy solutions; Technologies for energy symbiosis Enterprise 4.0: integrated, innovative, and multi-scale design; Automation and collaborative robotics; Agile reconfiguration, human-centric and inclusive workspaces; sensors; AI Digital solutions; Additive manufacturing) |
 Central Greece (EL64), Greece Central Greece (EL64), Greece |  | • Sustainable Energy (Green innovation, energy efficiency and production from RES and biofuels) • Environment & Circular Economy (Reduction of the ecological footprint in agriculture, livestock breeding, processing and tourism) • Materials, Constructions and Industry (Supporting the Metal Value Chain, development of industrial areas) |
 Attica (EL30), Greece Attica (EL30), Greece |  | • Biosciences, Health and Pharmaceuticals (Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare, biotechnology) • Environment & Circular Economy (Focus on energy and environment, smart foods) • Agri-Food Value Chain (Improvement of primary production products, Rational management of natural resources; Nutrition, Health, Consumers, Aquatic Biotechnology) |